NAD Guide
With this guide, you will be able to find more about
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+).
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
NAD is a compound which is found in all living cells. This small molecule is a core essential for life. It plays many essential roles during the metabolic process, where it turns nutrients into energy.
As we get older the levels of NAD in our bodies start to decline, however researchers have found ways to boot the NAD+ levels in the body through supplementation. Studies have shown many health benefits associated with nicotinamide riboside, it has shown significant results in maintaining a robust heath, and preventing problems which accompany aging.


NAD+ Explained
According to Sciencemag.com, NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an essential part for life. It is a co-enzyme which is found in all living cells. Just as important to us as the air we breathe and the food we eat.
Science has shown that NAD+ levels start to decrease as we get older, the higher our levels of NAD+ are the better our cells function. Scientists believe that our health and lifespan can be improved with a supplementation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
NAD+ History
NAD+ was discovered in 1906, by two British biochemists, Arthur Harden and William John Young. The importance and medical benefits where then established when a disease called pellagra was discovered. Pellagra, a disease, caused by a severe lack of vitamin B3. Typical symptoms include, diarrhoea, inflamed skin, mouth sores and even dementia. Pellagra can be fatal if left untreated. Although not a common disease, NAD+ has shown helpful in halting age associated diseases and assist with slowing down the aging process.
NAD+ has been administered as early as the 1930’s. It has found to improve the neurological state of dementia patients and has been found to provide dramatic therapeutic benefits for diseases such as schizophrenia, colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and muscular sclerosis (MS).
Recent Science Supports the Benefits of NAD+
While NAD+ has been around for more than a century, only in recent years have some major discoveries surrounding NAD+ been made. While we are aware that the involvement of NAD+ with increasing energy metabolism and mitochondrial functions, it has recently been discovered that NAD+ has been linked with DNA repair and can assist in longevity of life.
Amongst these discoveries, it was found that NAD+ levels slowly decline as we age. Meaning the processes within the body, which require NAD+, may not function properly as we get older.
An American biologist, Dr Leonard Guarente discovered that, a family of proteins which keep our cells in homeostasis, governing longevity, only functioned when NAD+ was present.
In a recent study “ NAD+ metabolism and oxidative stress “ it was found that NAD+ was identified as a very important factor in cellular respiration, generating energy production and playing a somewhat unique role in the repairing of DNA. NAD+ plays a significant role in oxidative stress, immune activation, cell viability in neurodegenerative disorders and energy metabolism. Administering NAD+ into the body can effectively regulate stress resistance and cell death, which are associated with age related disorders. Studies show that as human beings our goal is to stay in a state of balance, a state of homeostasis. Made possible by specific proteins and coenzymes.
Sirtuins, What are they?
Sirtuin rich foods have proven to provide an array of heath benefits. Improving life quality and longevity. Sirtuins are a family of age-related proteins, this help reduce inflammation, regulate metabolism, and are linked with improving cellular death. Sirtuins can also improve the functions of memory formation and modulate the plasticity of the brain.
The top sirtfoods

Kale
A single cup of raw kale (about 67 grams or 2.4 ounces) contains:
* Vitamin A: 206% of the DV (from beta-carotene)
* Vitamin K: 684% of the DV
* Vitamin C: 134% of the DV
* Vitamin B6: 9% of the DV
* Manganese: 26% of the DV
* Calcium: 9% of the DV
* Copper: 10% of the DV
* Potassium: 9% of the DV
* Magnesium: 6% of the DV
SOURCE

Red Onion
They also contain anthocyanins, which are plant pigments that cause the deep red colour of the onions. Studies have found that consuming foods rich in anthocyanins have a lessened risk of heart disease.
Onions are also low in calories but rich in vitamins, such as Vitamin B and Vitamin C.
SOURCE
SOURCE 2
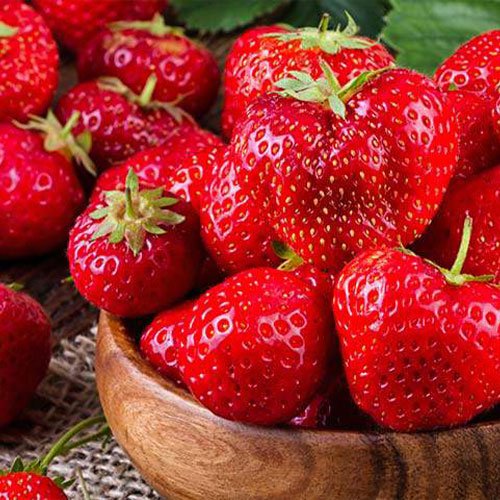

Strawberries
They are high in water content (91%) - so they contain very low amounts of fat (only 0.3%). They’re also low in calories - 100 grams of fresh strawberries only contains 32 calories.
Of the carb content of strawberries, around 26% of it is comprised of fiber. This is great for improving your digestive health. Strawberries also are loaded with antioxidants, including anthocyanins.
SOURCE
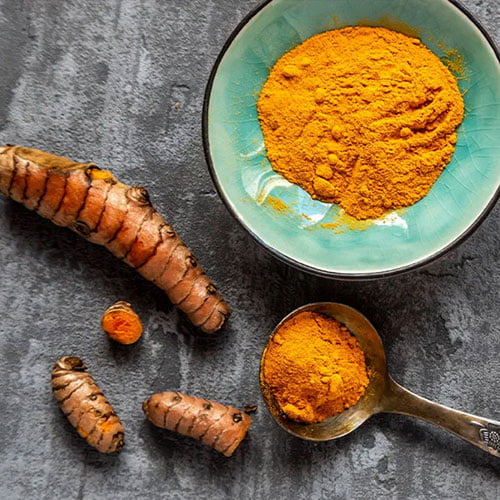

Tumeric
Curcumin can also increase brain levels of BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), which is a growth hormone functioning inside your brain. Brain diseases and disorders (such as Alzheimer’s Disease and depression) have been associated with lower levels of this hormone.
SOURCE
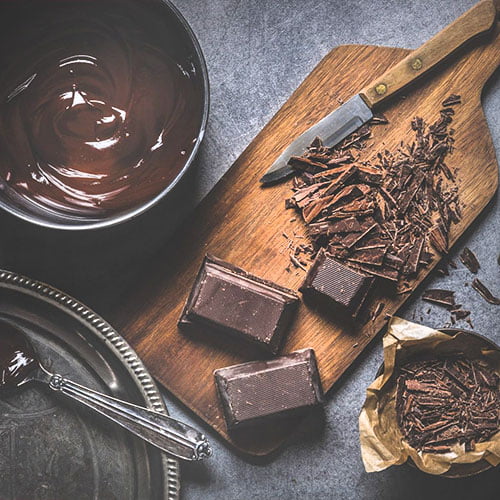

Chocolate
It also is packed with organic compounds that function as antioxidants - such as polyphenols, catechins and flavanols.
Many studies have also shown that dark chocolate can lower blood pressure and also improve blood flow.
SOURCE
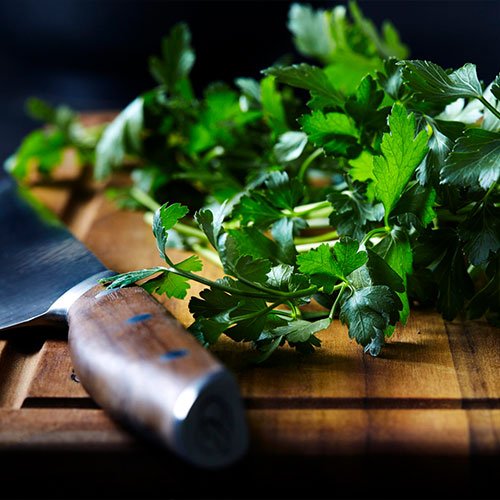

Parsley
Parsley is a flavour-packed herb that is easy to incorporate into a variety of dishes, and it is very low in calories. It’s also rich in antioxidants (such as carotenoids and flavonoids), therefore possibly helping to reduce free radicals.
Lastly, parsley contains three carotenoids (lutein, beta carotene and zeaxanthin) that can help protect your eye health and vision.
SOURCE
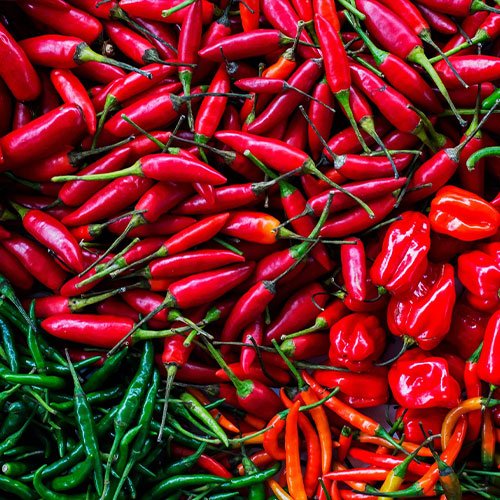

Chilli
They contain a variety of vitamins and minerals, including Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, Vitamin K1, potassium, copper and Vitamin A.
Some other important bioactive plant compounds in chilli peppers are: capsanthin (which has antioxidant properties that may be able to fight cancer), lutein (which can help eye health) and ferulic acid (an antioxidant that may help protect against various diseases).
SOURCE
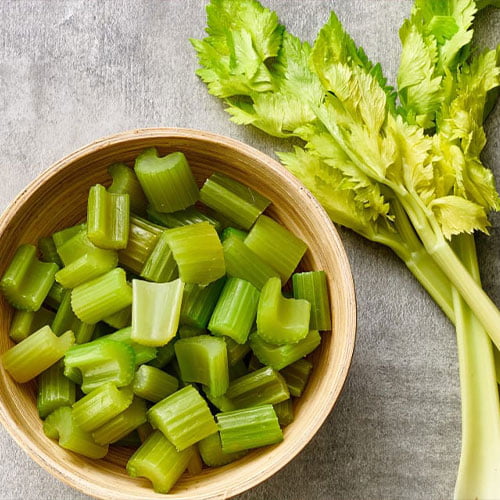

Celery
It contains antioxidants that protect organs and cells from oxidative damage. It is a powerhouse of vitamin C, beta carotene and flavonoids, and it also contains phytonutrients (which can reduce inflammation in the body). Celery (and its seeds) have around 25 different anti-inflammatory compounds.
Celery also has generous amounts of fiber, which can help with digestion.
SOURCE
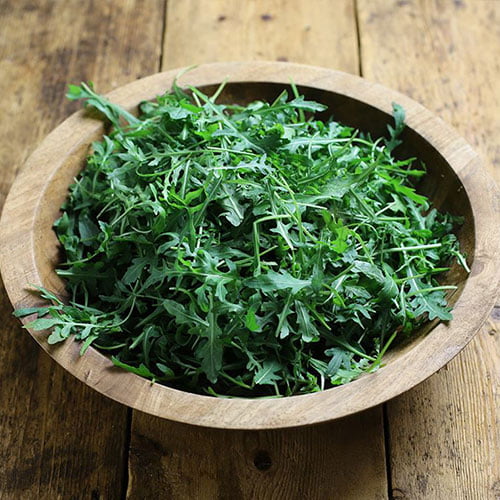

Rocket
It contains calcium, potassium, folate, Vitamin C, Vitamin K and Vitamin A, so it’s safe to say that rocket is a nutrient powerhouse.
SOURCE
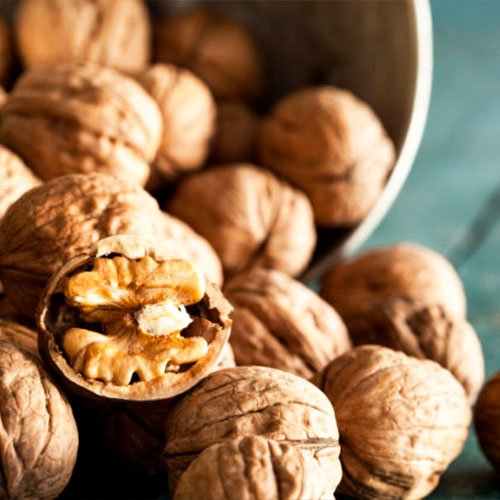

Walnuts
Some studies conducted have shown that walnuts may even help to lower blood pressure and support healthy brain function.
SOURCE